Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing the medical field, transforming healthcare through:
These applications significantly enhance patient outcomes and operational efficiency. AI technologies not only improve diagnostic accuracy but also streamline workflows and facilitate proactive patient management.
However, the journey toward integration is not without challenges. Issues such as:
must be addressed to ensure responsible implementation. By navigating these challenges, healthcare organizations can harness the full potential of AI, leading to improved care delivery and operational excellence.
The integration of artificial intelligence into the medical field is not merely a passing trend; it signifies a seismic shift in the delivery and management of healthcare. With the capacity to analyze vast amounts of data, AI technologies are enhancing diagnostic accuracy, streamlining administrative tasks, and ultimately improving patient outcomes. However, as the adoption of AI in healthcare accelerates, it raises critical questions regarding:
These issues must be addressed. How can the medical community harness the power of AI while ensuring equitable and responsible care for all patients?
Artificial intelligence in the medical field involves the use of advanced algorithms and software designed to replicate human reasoning in analyzing, interpreting, and managing complex medical information. This field encompasses:
These technologies collectively enhance diagnostic accuracy, streamline administrative tasks, and improve patient outcomes. AI systems are capable of processing vast amounts of data from:
This capability allows healthcare providers to make informed decisions quickly and effectively. For instance, Inferscience’s API solution facilitates seamless HCC coding information exchange among providers, payers, and third-party vendors, addressing interoperability challenges and improving patient outcomes. Additionally, the Claims Assistant tool performs real-time gap analysis on claims files, suggesting HCC codes that enhance billing accuracy and provide clearer insights into individual conditions. By consolidating information and optimizing risk adjustment processes, these AI-driven solutions significantly increase efficiency and compliance within the artificial intelligence in the medical field.

The application of artificial intelligence in the medical field is fundamentally transforming medical practice through several key applications that address existing inefficiencies and enhance patient care.
Diagnostic Assistance: Advanced AI algorithms excel at analyzing medical images, such as X-rays and MRIs, to identify anomalies that may elude human detection. This capability significantly enhances diagnostic accuracy, with studies indicating that AI can halve the time for stroke victims to receive treatment, thereby improving their chances of recovery.
Predictive Analytics: Utilizing historical individual data, AI systems can anticipate future health events, enabling care providers to adopt proactive management strategies. The implementation of AI-driven tracking systems for individuals has led to a 27 percent reduction in long-waiters and an eight percent decrease in emergency admissions, showcasing the effectiveness of predictive analytics in managing care.
Clinical Decision Support: AI tools furnish medical professionals with evidence-based suggestions, refining the decision-making process. This support is crucial in complex situations where timely and precise decisions can greatly influence outcomes for individuals.
Administrative Automation: AI streamlines various administrative tasks, including scheduling, billing, and coding. Inferscience’s HCC Assistant, which employs advanced natural language processing (NLP) and intelligent rules, eliminates almost all manual effort from HCC coding workflows. This automation reduces the administrative load on medical personnel, allowing them to concentrate more on patient care. Furthermore, the integration of AI in coding processes has been shown to enhance accuracy and consistency, ultimately leading to better compliance and funding outcomes, ensuring providers receive maximum funding from Medicare Advantage contracts.
Telemedicine: AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants enhance interactions by providing instant replies to queries and aiding in triage processes. This technology not only boosts user engagement but also optimizes resource distribution in medical settings.
As AI continues to develop, its applications in medical care are expected to expand, fostering further innovations and enhancements in patient care.
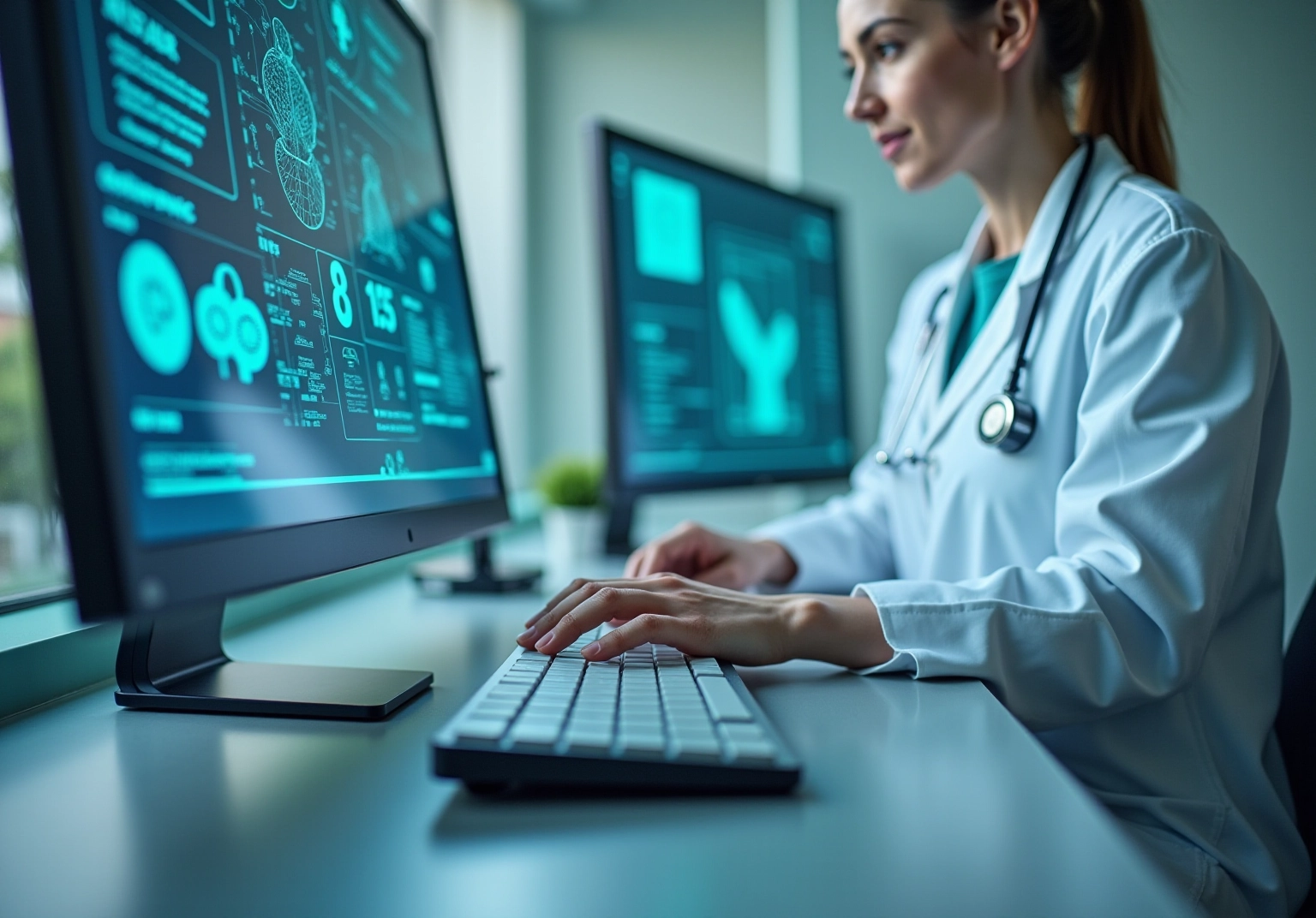
While artificial intelligence in the medical field offers numerous benefits, it also presents significant challenges and ethical considerations that must be addressed.
Data Privacy: The integration of AI in healthcare necessitates access to sensitive patient data, raising critical concerns about data security and patient confidentiality. Ensuring strong information protection measures is essential to maintain trust and comply with privacy regulations.
Bias and Fairness: AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate existing biases if trained on non-representative datasets. This can lead to disparities in care, particularly affecting marginalized populations. Recent studies emphasize that biased algorithms can lead to misdiagnoses and unequal treatment results, highlighting the necessity for varied training information. Research has indicated that algorithms primarily trained on information from affluent nations may not function effectively in low- and middle-income environments, resulting in notable inequalities in medical service provision.
Transparency: The ‘black box’ nature of certain AI algorithms complicates the understanding of decision-making processes in medical settings. This absence of clarity can obstruct responsibility and make it difficult for service providers to clarify AI-driven choices to individuals, potentially undermining confidence in these technologies. Experts stress that without clear insights into how AI systems function, it becomes challenging to ensure accountability and cultivate trust among users and providers alike.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring that AI applications adhere to medical regulations and standards is crucial to avoid legal repercussions. As AI technologies evolve, regulatory bodies must adapt to oversee their implementation effectively, safeguarding patient rights and interests. The European Union is currently considering a formal regulatory framework for the ethical use of AI, which highlights the need for comprehensive guidelines to govern AI applications in healthcare.
Patient Consent: Patients must be adequately informed about how their information is utilized in AI systems. Clear communication and consent procedures are essential to empower individuals and maintain ethical standards in data usage. This includes addressing concerns about how AI may influence their care and treatment decisions. Experts contend that informed consent is not merely a legal necessity but a core ethical duty that honors individual autonomy.
Tackling these ethical factors is crucial for the responsible implementation of AI in medical settings, ensuring that technological progress improves care without undermining ethical principles.

The future of AI in healthcare is poised for transformative advancements, particularly in several key areas that demand attention:
Integration with Genomics: AI is set to revolutionize the analysis of genomic data, paving the way for personalized medicine that aligns treatment plans with individual genetic profiles. This integration enhances the precision of therapies, allowing for tailored interventions that significantly improve outcomes for individuals.
Enhanced Telehealth Solutions: The evolution of AI will substantially bolster telehealth platforms, facilitating more accurate remote diagnostics and continuous patient monitoring. By leveraging AI algorithms, healthcare providers can deliver timely interventions and maintain high-quality care, regardless of geographical barriers.
AI-Driven Drug Discovery: AI technologies are positioned to accelerate the drug discovery process by predicting interactions between various compounds and biological systems. This capability not only shortens the timeline for bringing new drugs to market but also enhances the effectiveness of treatments.
Robotics in Surgery: The integration of AI-powered robotic systems in surgical procedures will enhance precision and reduce recovery times for patients. These systems assist surgeons by providing real-time information and analytics, resulting in improved surgical outcomes.
Interoperability: Future AI systems will prioritize seamless integration with existing healthcare technologies, fostering enhanced information sharing and collaboration among providers. Inferscience’s API solution exemplifies this trend by simplifying HCC coding information exchange among providers, payers, and third-party vendors. The API utilizes intelligent rules for data extraction and delivers analysis in JSON format, enabling rapid retrieval of insights. This interoperability is vital for establishing a unified medical ecosystem that enhances care for individuals and operational efficiency.
As artificial intelligence in the medical field continues to evolve, its applications in healthcare will expand, driving innovations that enhance both clinical practices and patient experiences.

Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing the medical field by enhancing diagnostic capabilities, streamlining administrative tasks, and improving patient outcomes. The integration of advanced algorithms and machine learning technologies enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions rapidly, ultimately leading to more effective care. As AI continues to evolve, its potential to transform healthcare practices becomes increasingly evident.
Key applications of AI—such as diagnostic assistance, predictive analytics, and clinical decision support—showcase its ability to address inefficiencies and elevate patient care standards. Additionally, the ethical considerations surrounding data privacy, bias, and transparency highlight the importance of responsible AI implementation. Ensuring that AI systems are developed and utilized with ethical standards in mind is essential for maintaining trust and accountability within the healthcare sector.
Looking ahead, the future of AI in healthcare is filled with promise, from advancements in genomics to the integration of robotics in surgical procedures. Embracing these innovations will not only enhance clinical practices but also improve patient experiences. The ongoing dialogue about the ethical implications and regulatory frameworks surrounding AI will be crucial in shaping a healthcare landscape that prioritizes both technological progress and patient welfare.