
This article addresses the critical challenge of enhancing Risk Adjustment Factor (RAF) scores through precise Hierarchical Condition Category (HCC) coding. It underscores the necessity of:
These strategies are essential for ensuring accurate coding, which directly impacts funding levels and the financial sustainability of value-based care models. By adopting these measures, healthcare organizations can significantly enhance their RAF scores, ultimately leading to improved patient care and organizational success.
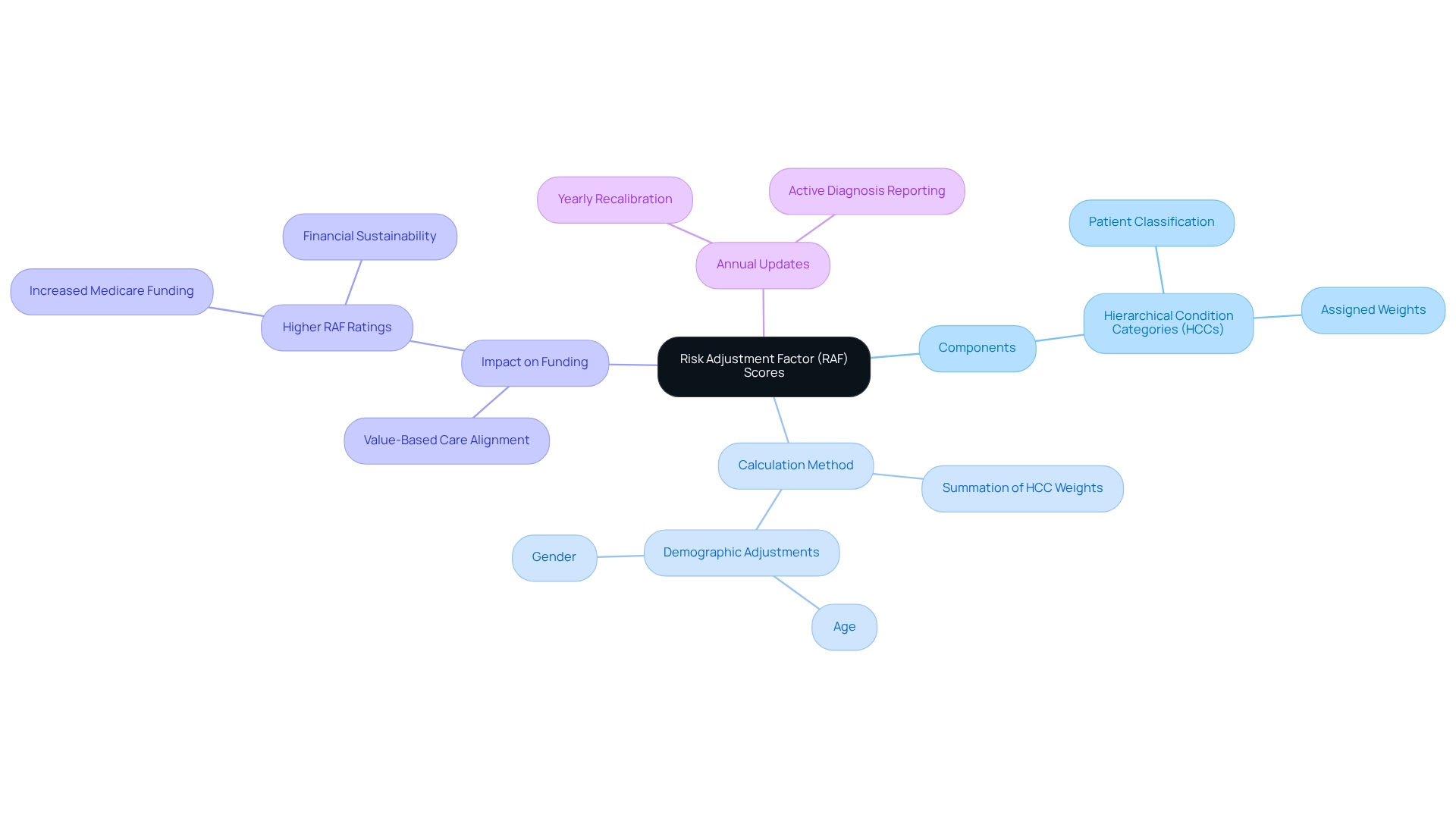
In the intricate realm of healthcare, grasping the significance of Risk Adjustment Factor (RAF) scores is imperative for providers striving to enhance their financial performance. These scores, which project anticipated healthcare costs based on patient demographics and health conditions, are critical in determining funding for Medicare Advantage plans.
Nevertheless, the path to achieving accurate RAF scores is riddled with obstacles, ranging from incomplete documentation to the complexities of coding guidelines. As healthcare organizations increasingly pivot towards value-based care, it becomes essential to master the subtleties of RAF scores and implement effective strategies.
This article explores the complexities of RAF scores, the challenges encountered in HCC coding accuracy, and the proactive measures that can improve both coding practices and financial sustainability in a dynamic healthcare landscape.
Risk Adjustment Factor (RAF) values serve as critical numerical indicators estimating expected healthcare costs for patients based on their health conditions and demographic characteristics. These values are instrumental in determining funding levels for Medicare Advantage plans. Understanding the key aspects of RAF scores is essential:
The integration of advanced NLP tools can significantly improve the accuracy of HCC coding by consolidating patient data from diverse sources, thus mitigating data silos that often result in inaccurate risk adjustment. Inferscience’s AI-driven solutions streamline these workflows, allowing providers to focus more on patient care rather than administrative tasks. Grasping the intricacies of RAF metrics is essential for medical providers to adeptly navigate the complexities of improving RAF scores. As Ryan Hakimi aptly states, “Overall, as organizations shift towards value-based care and delve deeper into informatics to quantify the cost of care provided, providers must recognize the potential for individualized compensation.” By mastering these concepts and leveraging advanced tools, providers can enhance their financial outcomes and ensure compliance with evolving medical regulations, ultimately improving RAF scores. The application of RAF metrics enables health plans to secure increased payments for elderly patients with various or serious conditions, aligning with the transition towards value-oriented care models within medical systems. As organizations increasingly adopt value-based care, the importance of precise RAF calculations cannot be overstated, as they directly influence compensation models and funding strategies.
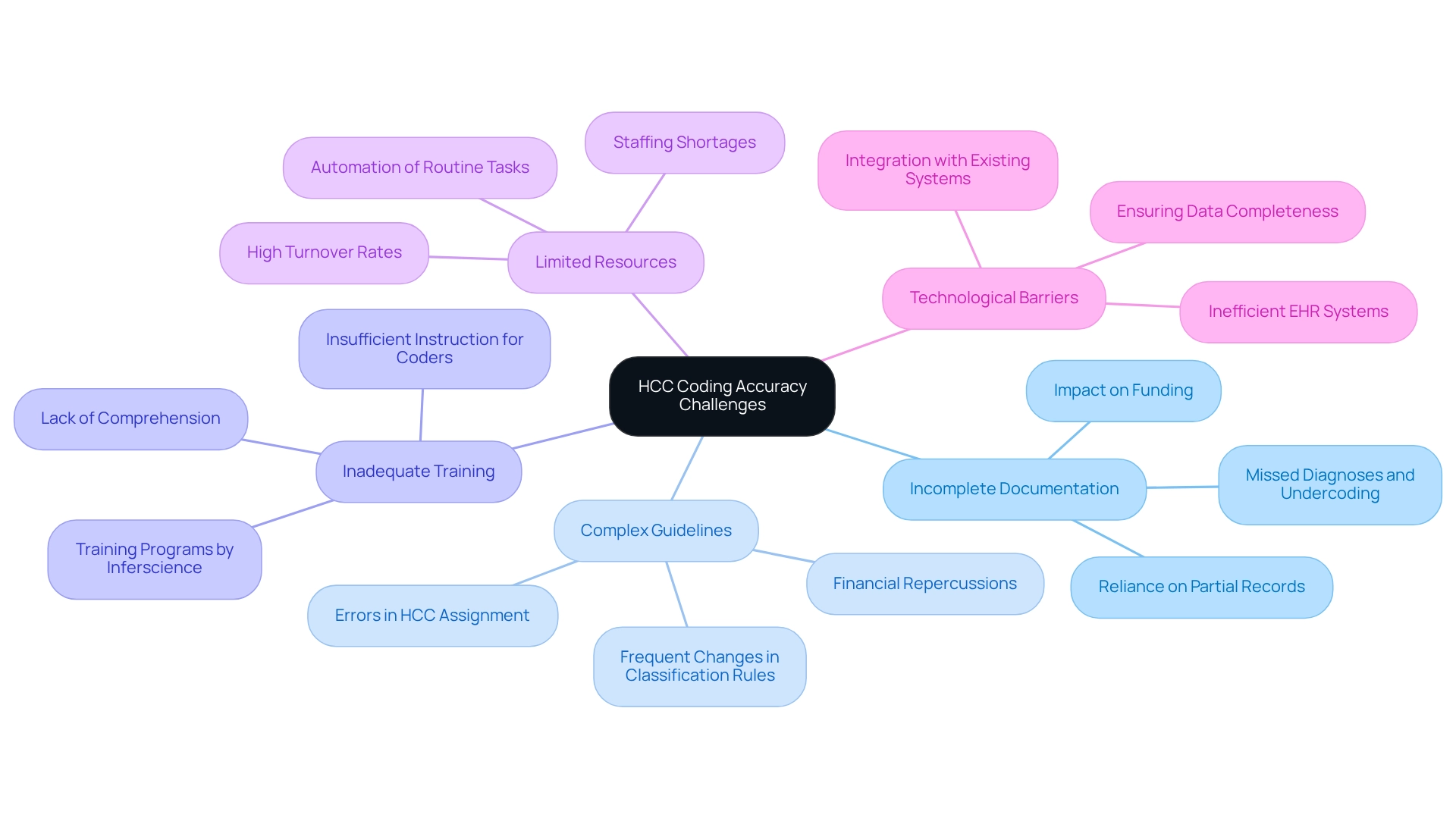
Accurate HCC documentation is essential for improving RAF scores related to Risk Adjustment Factor. However, healthcare providers frequently face significant challenges that can compromise accuracy. Key issues include:
Incomplete documentation is a primary challenge. The prevalence of incomplete clinical documentation often leaves coders reliant on partial patient records, resulting in missed diagnoses and undercoding, which ultimately affects funding. Inferscience’s AI-driven tools streamline documentation processes, ensuring that all relevant diagnoses are captured accurately.
The intricacies of programming guidelines can be daunting. Providers may struggle to stay informed with frequent changes in classification rules, leading to errors in HCC assignment and potential financial repercussions. Inferscience’s solutions leverage natural language processing (NLP) to simplify these guidelines, helping coders make informed decisions quickly.
Numerous healthcare organizations do not offer sufficient instruction for coders and clinicians, leading to a lack of comprehension about the essential nature of precise HCC classification. Inferscience addresses this gap by providing extensive training programs that equip staff with the knowledge required to improve accuracy in programming.
Staffing shortages and high turnover rates can severely affect the ability to uphold programming accuracy. Organizations may lack enough qualified staff to handle the required programming, worsening the problem. Inferscience’s technology alleviates some of this burden by automating routine tasks, allowing coders to focus on more complex cases.
Inefficient electronic health record (EHR) systems can complicate the documentation process, making it challenging to capture all relevant diagnoses. Inferscience’s advanced solutions integrate seamlessly with existing EHR systems, ensuring that data is complete and precise, which is essential for optimal results.
The effect of insufficient documentation on HCC classification is particularly evident, with research showing that false negatives can result in a 22% reduction in risk values. A case study analyzing conflicting claims within the Mass General Brigham ACO population demonstrated that reclassifying false-positive beneficiaries as true negatives would reduce average risk-adjustment values. This highlights the importance of accurate classification to ensure proper funding and resource distribution.
As Erin Page, President of Government & Value-Based Programs, states, “We strive to truly partner with our client organizations to ensure they have the tools they need to pivot through unexpected challenges and turn them into opportunities.” By recognizing these challenges and fostering teamwork, medical providers can adopt proactive strategies to improve their HCC classification precision, ultimately contributing to improving RAF scores and ensuring better financial outcomes. Furthermore, high denial rates may increase the need for costly rework and resubmissions, flagging organizations for audits and raising administrative burdens.
To enhance RAF scores through precise HCC coding, healthcare providers must consider several strategic initiatives:
By adopting these strategies, healthcare organizations can significantly enhance their HCC classification accuracy, ultimately leading to improving RAF scores and optimized funding from Medicare Advantage contracts. For instance, Allina Health’s proactive strategy for identifying discrepancies in documentation through EMR reports has demonstrated the effectiveness of targeted interventions in enhancing accuracy and aligning with patient needs. Furthermore, statistics indicate that incorrect programming can lead to substantial financial losses; a report suggested that primary care trusts may have faced approximately £1 billion in erroneous payments in 2010. This underscores the importance of effective documentation practices and continuous training in improving HCC classification accuracy and financial performance.
To maintain advancements in improving RAF scores, healthcare providers must establish a thorough monitoring and evaluation framework.
Understanding and effectively managing Risk Adjustment Factor (RAF) scores is crucial for healthcare providers aiming to improve their financial performance within the Medicare Advantage framework. This article delves into the intricacies of RAF scores, emphasizing their calculation through Hierarchical Condition Categories (HCCs) and the significant impact these scores have on funding. The challenges associated with HCC coding accuracy—such as incomplete documentation, complex guidelines, and insufficient training—are explored, highlighting the urgent need for proactive strategies to address these issues.
Implementing effective strategies, including:
can significantly improve RAF scores. By adopting these measures, healthcare organizations can enhance their coding accuracy, ultimately leading to optimized funding and better financial outcomes. Moreover, establishing a robust monitoring and evaluation framework is essential to sustain these improvements, allowing for continuous adaptation and engagement among all stakeholders involved.
In conclusion, mastering the complexities of RAF scores and HCC coding transcends mere compliance; it is a vital aspect of achieving financial sustainability in a value-based care environment. As healthcare continues to evolve, prioritizing accurate risk adjustment will empower providers to deliver better patient care while ensuring their organizations thrive financially.